20 years ago, Mars Global Surveyor was considered a pioneer among NASA spacecraft. But beyond that, he liked to encroach on the privacy of the other Martian robots.
Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) was a landmark mission of its time. After launch in 1976, NASA’s spacecraft began its journey to the Red Planet, becoming the first new spacecraft to reach its goal (November 7, 1996). He remained in orbit for 10 years until his “death”. The likely reason was the constant position of the battery, which was under direct sunlight, which led to the failure.
Although MGS is primarily remembered for his scientific contributions (including the detection of ravines that could be carved out of ancient water), he also captured quite a few spacecraft operating on Mars and around the planet at that time. Here are some of the most famous shots.
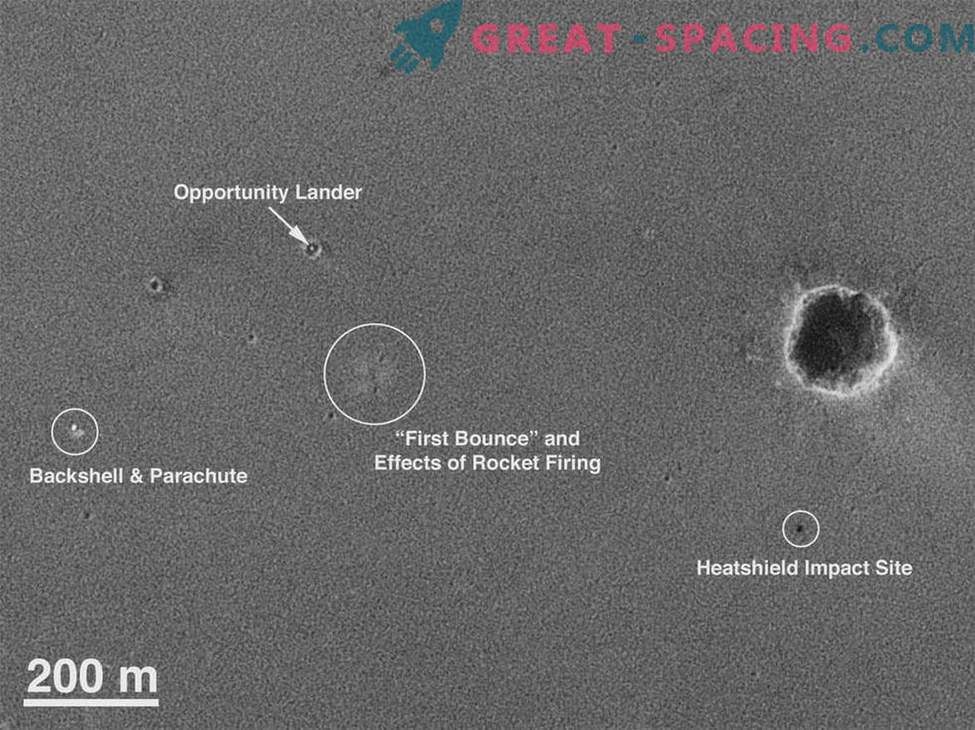

This image was taken shortly after the Opportunity rover landed in a small crater in January 2004. This feat at NASA was designated as “hitting the first strike.” Closer to the top of the image, you can see the rover peeking out from behind the crater. It is just north of the place where the rover's pillow first bounced off the surface. Nearby is a support body and a parachute from landing, as well as a noticeable blow from the heat shield. Opportunity is going to make a bold descent into a much steeper crater after a wonderfully spent 12 years on Mars. He found evidence of the presence of ancient water, covering a distance greater than the marathon race. He slowly moved from crater to crater, driven by a desire to find out as much as possible about the Martian past.
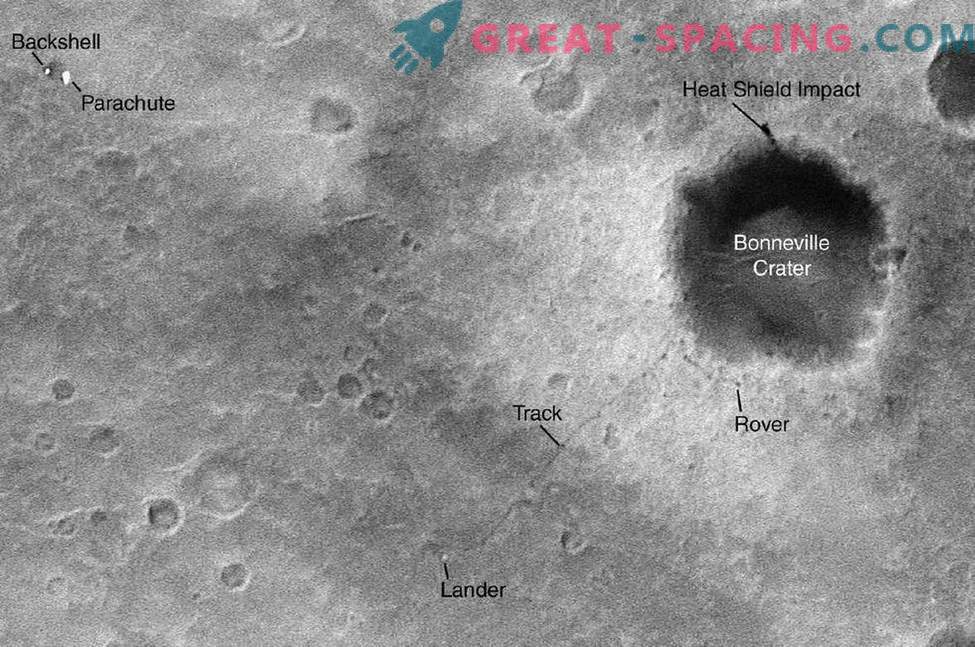

After just 85 Martian days after the sister of the Opportunity landed - the Spirit rover, MGS saw the rover at work, just when its main task, which lasted 3 months, was coming to an end. The tracks and the rover are south of the informally named Bonneville Crater. On the left side of the image there are places of impact from the supporting hull and a parachute, and on the north side of the crater there is a trace from a collision of a heat shield.
Spirit has successfully moved on the surface for 5 years. During this time, such discoveries were made as evidence of the presence of ancient streams of water on the surface, as well as tracking the influence of the Martian wind (for example, the mysterious Martian devil dust). In May 2009, the rover stuck in the soft regolith and could not get to the sunny place for the winter. After they failed to establish contact with the rover, NASA formally terminated the mission in May 2011.

This NASA Mars Odyssey image (Mars Odyssey) was made in 2005, when the spacecraft spent on Mars only a few years. Both Mars Global Surveyor and Odyssey were in ideal circular orbits that pass around the Martian poles. Sometimes they were so close that they separated only 9 miles (15 km). Odyssey was located slightly higher than the MGS to avoid collisions. Along with photos of Mars Express (below), it was one of the first “orbit-to-orbit” images taken on Mars. Odyssey is the premier communications compiler for the Opportunity rover and the new NASA Curiosity Mars rover that landed in 2012. He also managed to make several scientific discoveries. These include the detection of water ice directly below the Martian surface and images of Martian dust storms in 2007 and 2009.
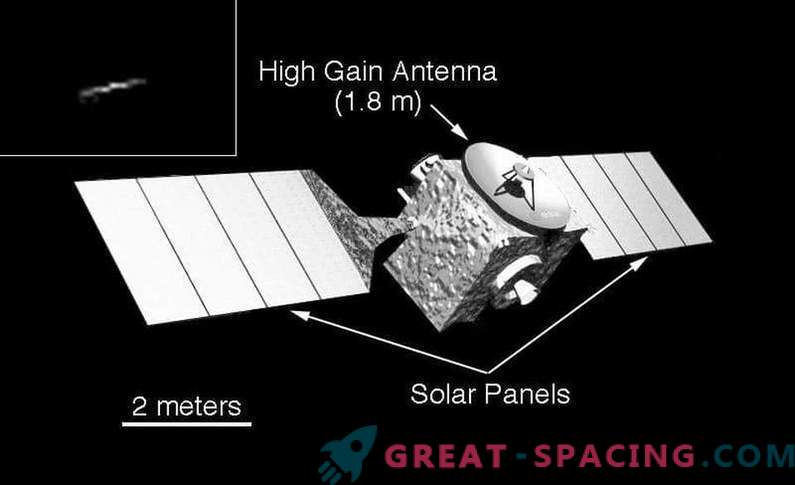
This is a combination of two images of the spacecraft of the European space agency Mars Express, taken from a distance of several hundred kilometers. Unclear outline due to the distance and the apparent movement of the Mars Express. But still it can be considered a feat. Along with the Odyssey images shown above, these were some of the first images of the orbit-to-orbit orbiter made on Mars.
Mars Express arrived in December 2003 along with the Beagle landing module (Beagle), which did not report to the ground that it had reached the surface. Mars Express continues to rotate around the planet, making discoveries. It is worth mentioning the tracking of polar ice on the surface, pictures of the Martian moon Phobos and the presence of methane in the atmosphere.
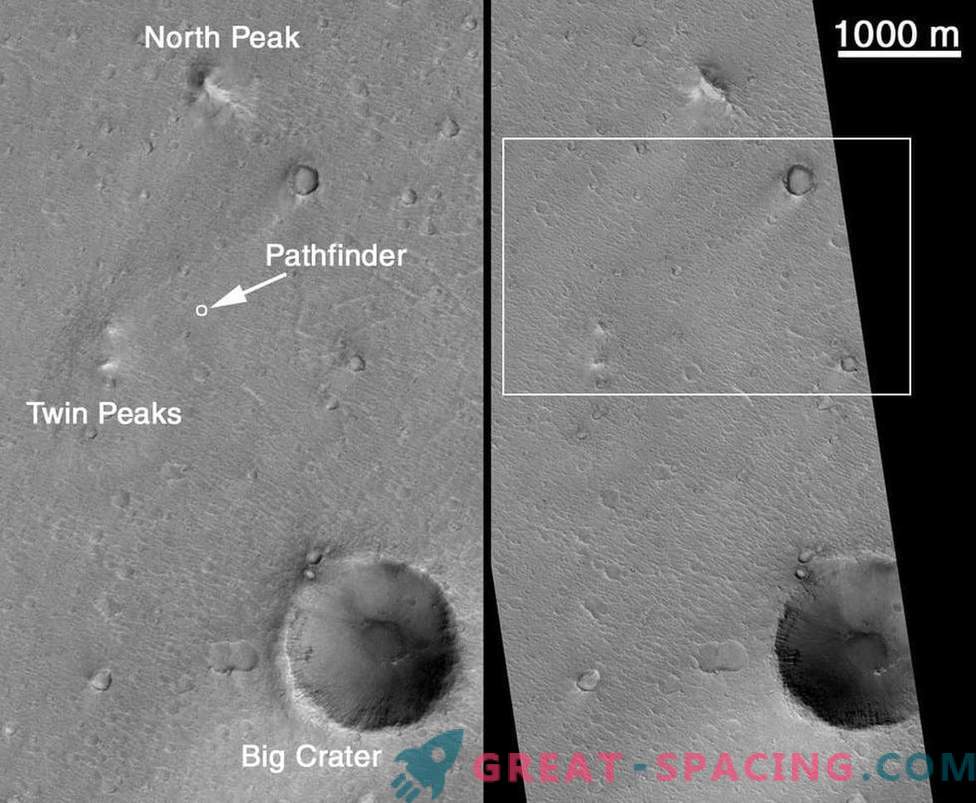

In January 2000, Malin Space Science Systems, which developed the Martian Orbital Chamber (MOS) for MGS, released a series of shots of the Sojourner rover and the location of the Pathfinder (Martian landing module). But the camera failed to capture the landing equipment itself. “While we manage to identify the landing site, the landing module itself remains out of sight,” said Malin Space Science Systems. “It is too small to be imprinted on an image, where each pixel of the camera covers an area of 1.5 meters (5 feet). Moreover, it is worth considering the contrast between the conditions on Mars and the capabilities of the MOC orbital camera. ” Fortunately, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter station managed to take pictures of the place in 2006, where both the rover and the landing module are visible. Sojourner was the first rover on the planet, and in the public mind, he was again popularized in 2015 in the film “Martian”, where he was discovered by the main character Mark Watney (Matt Damon). One of the main findings of the mission was a “conglomerate” of stones and pebbles, which were signs of something (for example, water).