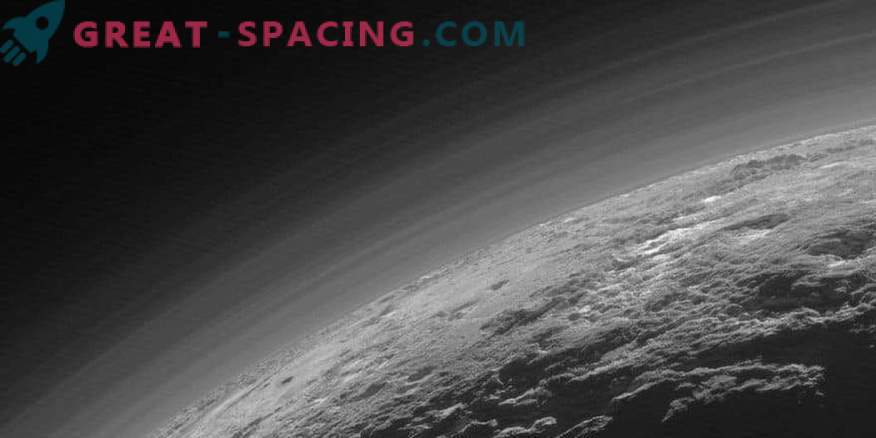
The artistic interpretation of Charon through the atmospheric layers of Pluto over the mountain landscape of water ice, partially covered by a dark and reddish haze
Usually it is the gas composition of the atmosphere that determines how much heat enters the layer. But the unpredictable temperature of the dwarf planet Pluto is based on atmospheric composition. It was higher than the figures for New Horizons, taken in 2015.
The new study decided to explore the mechanism of cooling haze. The process includes the absorption of heat by particles of smoke, which then emit infrared light, lowering the degree of the atmosphere and radiating energy into space. As a result, the forecasts showed -173 ° C, and the actual measurements reach -203 ° C.
Scientists believe that the excess infrared radiation of the particles can be fixed by the future telescope of James Webb. This will confirm the hypothesis after the start in 2019.

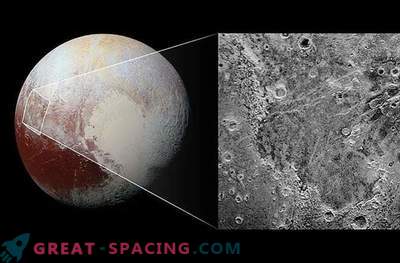
The image shows Pluto's haze layers captured by the New Horizons camera. Attenuation created by sunlight and chemical reactions of methane and nitrogen
Shooting from the device New Horizons perfectly demonstrated layers of atmospheric haze. Blackout occurs due to chemical reactions in the upper atmospheric layer, where the sun's UV light ionizes nitrogen and methane. As the tiny particles dive into the atmosphere, they stick together and form aggregates that grow during descent and settle to the surface.
It is believed that the hydrocarbon particles are responsible for the creation of reddish and brown material on the surface. Researchers are also interested in studying the effect of haze particles on the atmospheric energy balance of other planetary bodies, such as Triton (Neptune’s moon) and Titan (Saturn’s moon).